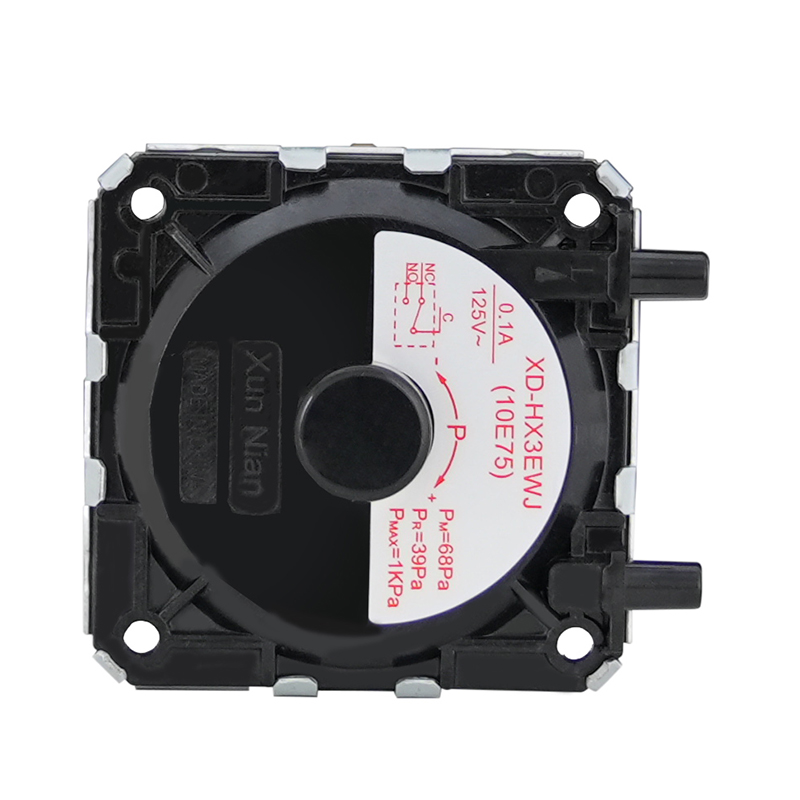
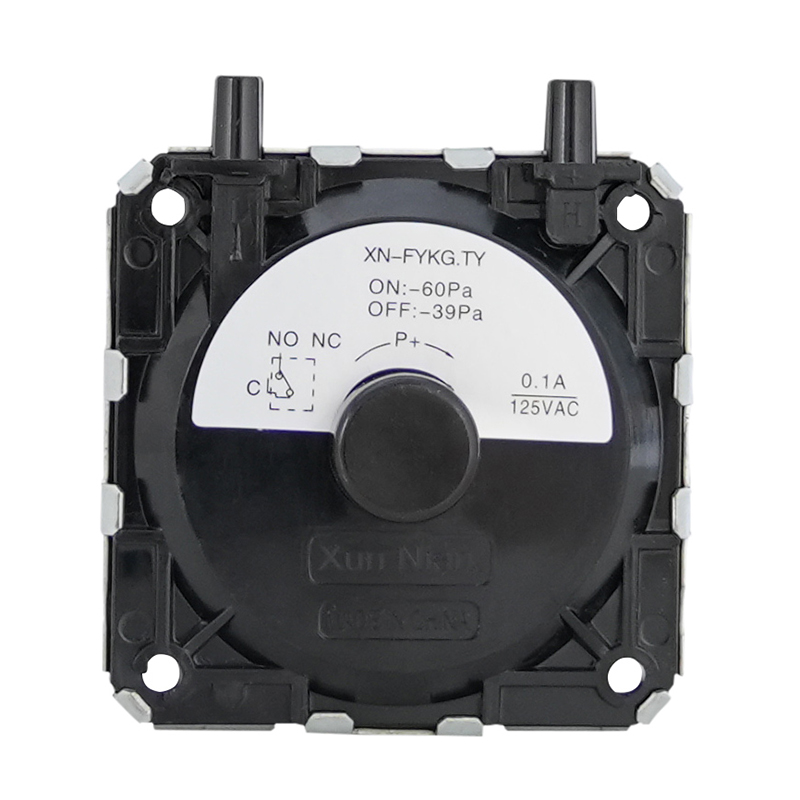
In the safe operation chain of gas equipment, the air pressure switch is like a "nerve center", and its working state is directly related to the stability and safety of the equipment. It can automatically connect or disconnect the circuit according to changes in air pressure, thereby realizing the protection and control of the equipment. Judging whether the air pressure switch is working normally is crucial to ensuring the safe operation of the equipment.
Inspection of Appearance and Basic Status
1.Physical Damage Inspection
Before conducting any testing, an intuitive inspection of the air pressure switch should first be carried out. Check if the appearance of the switch has obvious damage, such as cracks, deformation, or corrosion. At the same time, check if the terminal blocks are loose or corroded to ensure good electrical connections.
2.Reset Function Test
Some air pressure switches are equipped with a manual reset button (especially in industrial equipment). When the equipment is shut down, press the reset button to see if there is a distinct "click" sound. If the button has no feedback or is stuck, the internal mechanical structure may be jammed, requiring timely maintenance.

Functional Judgment Combined with Equipment Operation Status
1. Judgment During the Start-up Phase
When the equipment starts, the air pressure switch should respond quickly after the gas pressure reaches the start-up threshold:
· Normal situation: At the moment of ignition, the equipment has no abnormal noise, the burner works stably, and the pressure gauge pointer (if any) is stable within the normal range;
· Abnormal situation: If there is a "ignition failure" prompt, frequent restarting, or immediate shutdown after start-up, it may be that the air pressure switch does not detect sufficient pressure (such as insufficient pressure caused by pipeline blockage) or the contacts are stuck and cannot close.
2. Electrical Testing
Electrical testing can detect whether the electrical part of the air pressure switch is working properly. A multimeter can be used to measure the on-off state and resistance value of the switch.
(1) Measuring the on-off state: Set the multimeter to the on-off test mode and measure the on-off state between the two terminals of the air pressure switch. When the air pressure does not reach the set value, the low-pressure switch should be disconnected and the high-pressure switch should be connected; when the air pressure reaches the set value, the low-pressure switch should be connected and the high-pressure switch should be disconnected.

(2) Measuring the resistance value: Set the multimeter to the resistance measurement mode and measure the resistance value of the air pressure switch. Under normal circumstances, the resistance value should be close to 0Ω when the switch is on, and infinite when it is off. If the measurement results do not meet these standards, the switch may have an electrical fault.
Limit Pressure Test (Requires Professional Tools)
Connect a pressure gauge to the detection interface of the air pressure switch and gradually adjust the gas pressure:
· When the pressure is lower than the safety threshold, the switch should disconnect immediately, and the resistance between the contacts measured by the multimeter should be "infinite";
· When the pressure rises back to the start-up threshold, the contacts should close, and the resistance value approaches 0;
· If the pressure exceeds the threshold and there is no action, or the operating pressure deviates from the nameplate marking by more than ±10%, the switch has failed.
Judging whether the air pressure switch is working normally requires combining the understanding of principles, appearance inspection, functional testing, and professional instrument detection to form a complete judgment logic "from phenomenon to essence". For ordinary users, paying attention to abnormal signals during equipment operation (such as error codes, abnormal noises) and promptly contacting professional personnel for maintenance is the most reliable way. Regular maintenance can reduce the risk of failures from the source, ensuring that this "invisible guard" always maintains sharp perception and reliable protection capabilities.